Strengthening Healthcare Through Community Engagement: Insights and Innovations from GLC4HSR's Workshop
Updates ▪ Apr 26, 2024
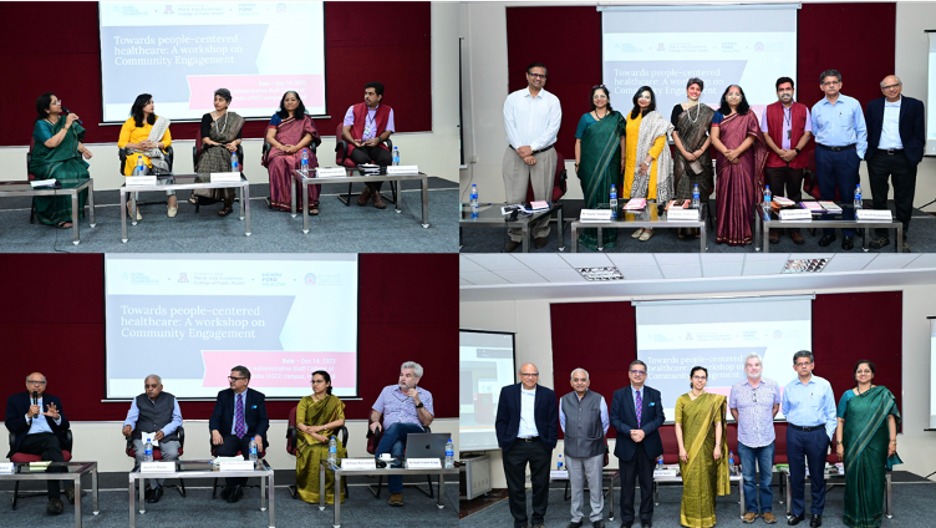
The Global Learning Collaborative for Health Systems Resilience (GLC4HSR) recently organized a workshop titled "Towards People-Centered Healthcare: A Workshop on Community Engagement." This half-day event, held in collaboration with the University of Arizona’s Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health, the Administrative Staff College of India (ASCI), and Henry Ford Health, featured esteemed speakers discussing the vital role of community engagement in building resilient health systems. The detailed summary report of the workshop can be found here. .
The workshop garnered active participation from over 150 attendees, both in person and online. The speakers delved into the role of community engagement in fostering more resilient health systems. Through insightful discussions, they provided clarity on the concept of community engagement and its practical implementation in real-world scenarios. The exploration also extended to understanding diverse community perspectives, including those of special interest groups, self-help groups, community health volunteers, civil society organizations, and the media.
The first session titled "Voices of the People: Exploring Diverse Perspectives on Community Participation Towards People-Centered Healthcare", delved into diverse perspectives on community participation in healthcare, revealing several key insights:
- Role of Community Engagement: Emphasized the trust-building aspect and understanding unique local needs for effective healthcare interventions. Communities play a crucial role in providing insights into their healthcare needs, which is foundational for developing targeted and sustainable healthcare programs.
- Broader Health Perspective: Advocated for addressing emotional, psychological, and societal aspects alongside clinical care. Healthcare delivery is not just about treating medical conditions but also about addressing holistic well-being, including mental health, social support, and community resilience.
- Technological Integration: Highlighted the potential of technology, like apps and online platforms, in training, data access, and service delivery. Technology can bridge gaps in healthcare access, especially in remote areas, and improve communication between healthcare providers and communities.
- Sustainable Funding Models: Addressed funding instabilities and the importance of sustainable models, leveraging cultural and social capital. Sustainable funding models ensure continuity of healthcare services, and leveraging cultural and social capital can enhance community participation and ownership in healthcare initiatives.
- Team-Based Care: Advocated for team-based care models, integrating frontline workers, specialists, and communities for better outcomes. Collaborative healthcare approaches ensure comprehensive care and improve health outcomes by addressing various aspects of health.
- Cultural Relevance: Emphasized culturally relevant practices, effective communication tailored to community nuances, and dispelling misconceptions. Cultural competence in healthcare delivery is essential for building trust, understanding health beliefs, and ensuring effective communication.
The second session titled, "Unpacking Community Engagement: Bridging the Gap from Concept to Reality", explored practical aspects of community engagement, offering the following insights:
- Community Empowerment: Highlighted the importance of community empowerment in engaging communities effectively. Empowered communities are more likely to actively participate in healthcare decision-making and initiatives, leading to better health outcomes.
- Adaptive Communications: Emphasized adaptive and accurate communication strategies in the post-COVID landscape. Effective communication is key to engaging diverse communities, especially in times of crisis or change.
- Human-Centered Care: Advocated for a culture of communication with patients and a human-centered approach to healthcare. Putting patients at the center of healthcare ensures personalized care and addresses individual needs and preferences.
- Healthcare Provider Role: Stressed that healthcare providers are part of the community, promoting trust and empowerment. Healthcare providers should be culturally competent, accessible, and empathetic to build strong relationships with communities.
- Decentralized Care: Advocated for decentralized care models to nurture communication and community engagement. Decentralization improves accessibility, responsiveness, and inclusivity in healthcare delivery.
- Community Governance: Active community participation in healthcare governance is essential for healthcare improvement. Engaging communities in decision-making ensures that healthcare services are responsive to community needs and preferences.
- Complex Implementation: While community engagement is crucial, its practical implementation remains complex. Effective community engagement requires collaboration, communication, and resource allocation to overcome barriers and challenges.
- Interconnected Roles: Various healthcare actors play interconnected roles in improving health outcomes. Collaboration between healthcare providers, community leaders, policymakers, and other stakeholders is essential for holistic and sustainable healthcare delivery.
- Broader Governance: Governance in healthcare should extend beyond government involvement to engage diverse stakeholders. Multisectoral collaboration, transparency, and accountability are key principles for effective healthcare governance.
- Patient-Centered Care: There's a shift towards patient-centered care, accompanied by challenges in creating a people-centric healthcare model. Patient-centered care emphasizes individual needs, preferences, and experiences to improve healthcare quality and outcomes.
- Technology Integration: Technology plays a crucial role in extending care to patients, emphasizing the need for a cohesive strategy in community engagement and healthcare governance. Leveraging technology can enhance access, efficiency, and quality of healthcare services.
The audience Q&A session added depth to the discussions, highlighting challenges and innovative solutions:
- Funding Challenges: Addressed efficient fund absorption mechanisms and public-private funding partnerships. Sustainable funding mechanisms are essential for maintaining healthcare services and addressing resource gaps.
- Mindset Shift in Healthcare: Discussed resistance within the healthcare profession towards patient-centric approaches and the need for a shift in mindset. Cultural change and training programs can help healthcare providers embrace patient-centered care.
- Tailored Urban Healthcare: Advocated for tailored solutions in urban healthcare delivery, emphasizing poverty, accessibility, and affordability challenges. Urban healthcare requires targeted strategies to address diverse populations and healthcare needs.
- Last-Mile Healthcare: Explored innovative approaches for providing healthcare to disadvantaged populations, focusing on community-specific needs. Tailored interventions and community partnerships are crucial for reaching underserved communities.
- Community Engagement Strategies: Emphasized the dynamic nature of community engagement and the importance of collaboration and knowledge sharing among stakeholders. Continuous learning, adaptation, and community participation are key to effective community engagement.
The workshop's discussions highlighted the critical role of community engagement in shaping resilient health systems, emphasizing effective communication strategies, collaborative approaches, and technology integration in healthcare governance. Understanding communities' capacity and addressing funding challenges are also crucial for sustainable healthcare delivery. Various healthcare stakeholders, including providers, community leaders, policymakers, and others, play interconnected roles in enhancing health outcomes, necessitating holistic and sustainable healthcare delivery through collaboration. Effective healthcare governance should involve diverse stakeholders beyond the government, focusing on multisectoral collaboration, transparency, and accountability to create a more equitable and inclusive healthcare landscape. The shift towards patient-centered care emphasizes individualized healthcare approaches, integrating patient needs and experiences for better outcomes. Additionally, technology integration is vital for extending care, necessitating a cohesive strategy in community engagement and healthcare governance to improve access, efficiency, and service quality. Translating these insights into actionable initiatives will be essential for building people-centered healthcare systems and improving health outcomes for all communities.
Written by Stuti Shukla, Lead, Communications, ACCESS Health International.